
In the realm of metallurgy, the composition of steel plays a pivotal role in determining its properties and behavior. Calcium, an essential element in this equation, exerts a notable influence on the melting temperature of steel. This article delves into the intricate relationship between calcium content and steel melting temperature, elucidating the mechanisms behind this interaction and its implications for various industries.
Calcium is often added to steel as a deoxidizing agent during the refining process. It reacts with oxygen to form calcium oxide (CaO), which, along with other impurities, becomes part of the slag layer. This reaction not only aids in the removal of undesirable elements but also affects the steel's overall composition. Calcium's presence can have a marked impact on the melting behavior of steel.
Lowering the Melting Temperature:
The addition of calcium to steel can lower its melting temperature, a phenomenon attributed to the formation of low-melting-point compounds. Calcium combines with other elements, such as sulfur and phosphorus, to create eutectic mixtures with notably reduced melting points compared to the pure metal. As a result, the incorporation of calcium in steel alters its phase transformation behavior and decreases the energy required for melting.
Eutectic mixtures, characterized by their lowest possible melting points, are pivotal in understanding the impact of calcium on steel melting temperature. The calcium-sulfur eutectic, for instance, forms at a specific composition and temperature, contributing to the overall decrease in melting temperature. Phase diagrams illustrating the equilibrium between different phases at varying compositions and temperatures provide insight into these eutectic interactions.
Practical Implications for Casting:
The influence of calcium on steel's melting temperature has significant implications for casting processes. The lowered melting temperature can simplify casting operations, reducing energy consumption and potentially extending the lifespan of casting equipment. Moreover, the decreased viscosity of the melt at lower temperatures can enhance fluidity and mold filling, leading to improved casting quality and reduced defects.
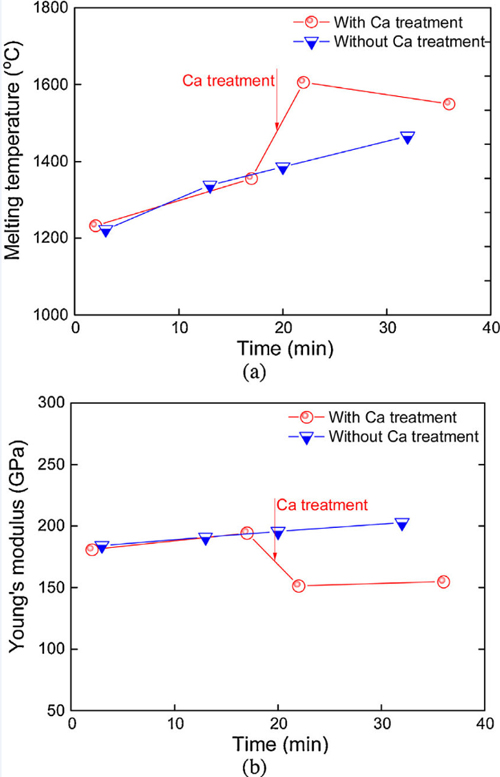
It's important to note that the impact of calcium on melting temperature is alloy-dependent. Different steel compositions respond differently to calcium additions, with the extent of temperature reduction varying based on the initial alloy components. Metallurgists must carefully consider the specific steel alloy and its intended application when determining the appropriate calcium content to achieve desired melting temperature effects.
While calcium offers the advantage of lowering melting temperatures, proper dosing is essential. Excessive calcium addition can lead to the formation of excessive inclusions, adversely affecting the steel's quality and mechanical properties. Moreover, the alloy's intended application and subsequent processing steps must be considered when adjusting calcium content to balance its effects on melting temperature and overall steel performance.
The relationship between calcium and steel melting temperature is a pivotal aspect of modern metallurgy. By introducing calcium into the steel composition, metallurgists can intentionally manipulate melting behavior, leading to practical advantages in casting operations and energy efficiency. Understanding the intricate mechanisms behind calcium's influence on melting temperature allows us to harness its potential while ensuring the optimal balance between alloy properties and processing requirements. As steel production continues to advance, the interplay between calcium content and melting temperature remains a critical consideration in shaping the materials of tomorrow.

Write a Message