
Corrosion, an insidious enemy of metal structures, poses significant challenges to industries relying on steel. In the battle against this formidable adversary, the integration of calcium has emerged as a potential solution. This article delves into the profound influence of calcium on steel's corrosion resistance, exploring how this element enhances durability and extends the lifespan of steel structures.
Corrosion is a natural electrochemical process that leads to the deterioration of metals due to reactions with their environment. In steel, corrosion manifests as rust – a phenomenon that weakens the material's structural integrity, compromises aesthetics, and increases maintenance costs. Addressing corrosion is of paramount importance in sectors such as construction, transportation, and infrastructure.
Calcium's Role in Corrosion Mitigation
In recent years, research has shed light on the positive impact of calcium on steel's corrosion resistance. Calcium-infused steel demonstrates enhanced resistance to corrosive elements, including moisture, oxygen, and various chemicals. This is largely attributed to the interaction between calcium and the steel's microstructure.
Formation of Protective Barriers
When calcium is present in steel, it facilitates the creation of protective barriers that shield the metal from corrosive agents. Calcium compounds react with elements like oxygen and sulfur to form stable oxides and sulfides, which act as protective layers. These layers serve as a physical barrier, limiting the exposure of the underlying steel to harmful substances.
Calcium's presence alters the composition of rust that forms on the surface of steel. Instead of flaky and porous rust, a more compact and adherent layer is produced. This modified rust layer not only provides better protection against further corrosion but also reduces the rate of rust propagation, extending the lifespan of the steel structure.
Mitigating Pitting Corrosion
Pitting corrosion is a particularly damaging form of corrosion, characterized by localized cavities on the metal surface. Calcium's influence can mitigate the occurrence of pitting corrosion by hindering the initiation and progression of these pits. The calcium-rich compounds create a less favorable environment for the development of aggressive corrosion cells, thereby safeguarding the steel from extensive damage.
Calcium's impact on corrosion resistance contributes to the long-term durability of steel structures. By minimizing the effects of corrosion, the need for frequent repairs and replacements is reduced. This not only enhances the economic viability of steel-based projects but also aligns with sustainable practices by reducing resource consumption and minimizing waste.
Application Challenges and Considerations
While calcium holds promise for improving corrosion resistance, its incorporation into steel production is not without challenges. Precise control over the calcium content and distribution is crucial to achieving the desired results. Excessive calcium can lead to negative effects on steel properties, underscoring the importance of careful formulation and application.
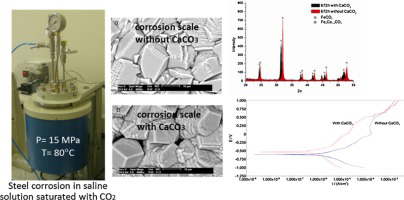
The incorporation of calcium into steel holds immense potential for enhancing corrosion resistance – a critical factor in maintaining the longevity and performance of steel structures. By forming protective barriers, altering rust composition, and mitigating pitting corrosion, calcium-infused steel exhibits a heightened ability to withstand the challenges posed by harsh environments. As industries continue to seek innovative solutions for durable and sustainable materials, the integration of calcium into steel production emerges as a promising strategy to combat the corrosive forces that threaten the integrity of steel structures.

Write a Message